Lymphatic Drainage Machines: The Complete Guide to At-Home Technologies
Let’s talk about that heavy, sluggish feeling. You know the one-where you feel puffy and swollen, no matter how much water you drink or how well you…

Let’s talk about that heavy, sluggish feeling. You know the one-where you feel puffy and swollen, no matter how much water you drink or how well you…
Are you tired of constantly cold hands and feet, no matter the season? Do you ever feel that frustrating brain fog that slows you down, or worry…

Does the ceiling look a little too familiar tonight? If you’re tired of the hollow advice to “just relax” or “avoid caffeine” while the exhaustion…

That constant, nagging ache in your lower back… it can feel like it runs your entire life. You want a natural solution, but the thought of…
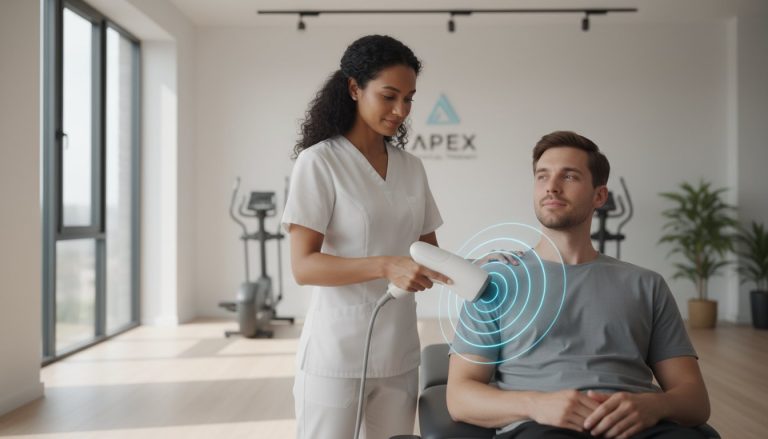

Living with persistent pain is frustrating enough without having to navigate a world of confusing treatments and technical jargon. You may have heard…

Do you constantly battle with icy hands and feet? Or maybe it’s that frustrating numbness, a persistent brain fog, or a general lack of energy that’s…

Have you looked at pre-made colloidal silver generators only to be put off by the shocking price tags? It’s a common frustration. You want the…

In a world full of confusing health advice and concerns about the side effects from long-term prescriptions, it’s no wonder so many of us are looking…

When a headache strikes, it can feel like your entire world shrinks to the size of that pulsing pain inside your head. The usual response is to reach…